What is Piles?
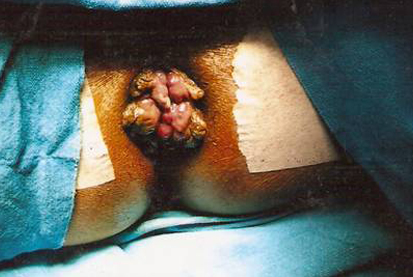
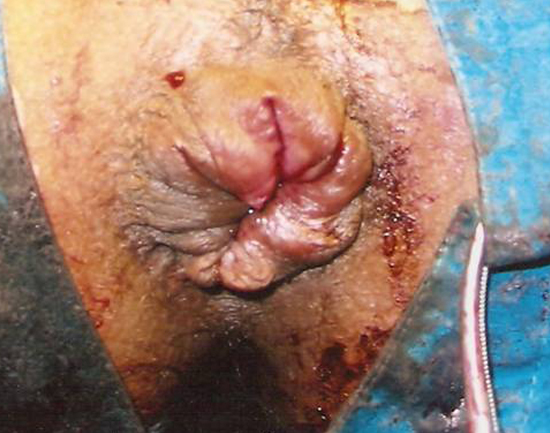
Piles are dilated ‘bunch’ of veins in the lower anal canal. Though Piles (Haemorrhoids) is one of the most common diseases afflicting human race yet the satisfactory treatment of this disease was largely unavailable for most of the times. Due to absence of single convincing treatment, the number of treatment options available today exceeds the number of myths surrounding the disease.
How is Piles caused?
Piles is a common problem affecting a large chunk of the population. It is estimated that 30% of population generally suffer from Piles during lifetime.
Constipation has been identified as the main cause of Piles. Pushing hard to pass stools puts a strain on the veins in the anal canal which eventually dilate and enlarge to form ‘piles’. Piles are more common in women during pregnancy and childbirth and there is some evidence that piles run in families.
What is the latest in the understanding of disease process of Piles?
Now the latest research has changed the way we look at piles. Earlier piles was thought to a dilated bunch of veins but now it has become clear that the basic defect in piles along with dilatation of veins is mucosal prolapse [ i.e. the inner covering layer(mucosa) of rectum becomes loose and that’s why it protrudes out]. This understanding of the disease process has led to the improved treatment. Earlier all treatment of piles i.e. Banding, Cryotherapy, Injection treatment, Trans rectal Doppler haemorrhoidal ligation (THD)and conventional surgery removed or treated bunch of dilated veins(piles) without addressing the basic cause i.e mucosal prolapse. Stapler haemorrhoidectomy is the only treatment modality available today which by removing 1-2 cm of mucosal cuff corrects the underlying basic pathology while giving painless relief to problem of piles at the same time.
What are the symptoms of Piles?
- Pain or ache around the anus and lower bowel (rectum), which can be really quite severe.
- There may be itching of the area especially after passing motions.
- There may be bleeding from the back passage. This will be bright red blood, not usually mixed in with the motion, but often seen on the toilet paper.
- There is often a feeling of something coming down, or a bulge or lump at the anus.
- If a haemorrhoid at the outside of the anus gets a blood clot in it (thrombosed external pile) it leads to a particularly tender, hardish lump.
How is Piles diagnosed?
Most episodes of trouble from haemorrhoids come and go quite quickly. If simple measures do not help or the problem is lasting, keeps returning or worsening, then you should see your doctor, especially if you have any other associated symptoms eg weight loss; change of bowel habit; slime (mucus) in the motions; darker, changed blood mixed in with the stools.
Your doctor will ask a few questions and is likely to examine you and may want to feel inside the anus with a gloved finger. Sometimes he will look inside with a metal instrument. This enables him or her to confirm the diagnosis, and to rule out other, more serious problems such as cancer.
How is Grading or Surgical Classification of Hemorrhoids(Piles) done?
Hemorrhoids (piles) arise from congestion of internal and/or external venous plexuses around the anal canal. They are classified, depending on severity, into four degrees. First degree hemorrhoids bleed but do not prolapse outside of the anal canal; second degree prolapse outside of the anal canal, usually upon defecation, but retract spontaneously. Third degree hemorrhoids require manual placement back inside of the anal canal after prolapsing, and fourth degree hemorrhoids consist of prolapsed tissue that cannot be manually replaced and is usually strangulated or thrombosed.
What is the treatment of Piles?
In the initial stages, a lot of treatment options are available such as high fibre diet, Banding[place small rubber bands around the hemorrhoids to cut off the blood supply], Sclerothrapy [inject the hemorrhoids with a drug that drastically shrinks them], Cryotherapy[the hemorrhoid is essentially frozen off], Infra-red coagulation or laser[the hemorrhoid is burned off, cauterizing the ends] etc. These modalities provide good relief in initial stages but do not help much in the later stages of the disease. In advanced stage, only Surgery provides long lasting relief. Now Stapler method of treatment has revolutionized the surgical treatment of piles.
What is Rubber Banding technique to treat piles?
A special instrument fits a small rubber band over part of the hemorrhoid. A tight rubber band stops the blood flow into the pinched-off portion, which falls off in about a week. This technique is widely used for hemorrhoids protruding into the anal canal.
For patients with a lesser degree of prolapse, Rubber Band Ligation is currently the most widely used procedure all over the world for treatment of internal hemorrhoids. In this procedure, the hemorrhoidal tissue is pulled into a double sleeved cylinder to allow the placement of latex/rubber bands around the tissue. (fig. 1) Overtime, the tissue below the bands dies off and is eliminated during a bowel movement. (fig. 2)…Read More
What is Cryotherapy?
A cryogenic device uses liquid nitrogen to super freeze the hemorrhoid. This causes the affected tissue to slough off, so that new healthy tissue can grow in its place. This technique is most effective when it is used on external hemorrhoid.
What is Bipolar Coagulation?
Bipolar electrotherapy is applied for a directed coagulation effect of the mucous membrane near the hemorrhoid. Specialized Bipolar Circumactive Probes (BICAP) are effective for the treatment of bleeding internal hemorrhoids. Bipolar electrotherapy is applied for a directed coagulation effect of the mucous membrane near the hemorrhoid. Specialized probe designs are effective for the treatment of bleeding internal hemorrhoids.
What is DHAL [Doppler Hemorrhoidal Arterial Ligation]?
Doppler Hemorrhoidal Arterial Ligation (H.A.L.) is performed using a modified proctoscope in conjunction with a Doppler ultrasound flow meter. A needle and thread is passed beneath the artery, and a knot is externally tied, to stop the blood flow to the hemorrhoid.
What is Sclerotherapy or Injection treatment ?
To shrink the hemorrhoid and its blood vessels, medicine (Phenol in Almond oil) is injected into the mucous membrane near the hemorrhoid. This medicine causes sclerosis (thrombosis/clotting) of veins. This method is reserved for the smallest of hemorrhoids.
What is Hemorrhoidolysis?
Therapeutic galvanic waves applied directly to the hemorrhoid(piles), produces a chemical reaction that shrinks and dissolves hemorrhoidal tissue. This technique is most effective when it is used on internal hemorrhoids.
What is Photocoagulation?
A device called a photo coagulator focuses infrared light into a fine point at the end of a probe, which spot welds the hemorrhoid in place. This is used for hemorrhoids that are actively bleeding.
What are surgical options available to treat Piles?
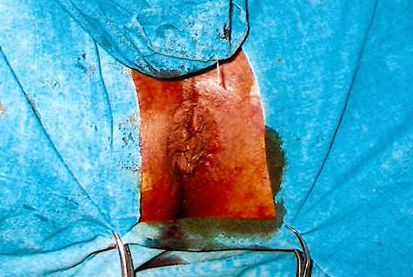
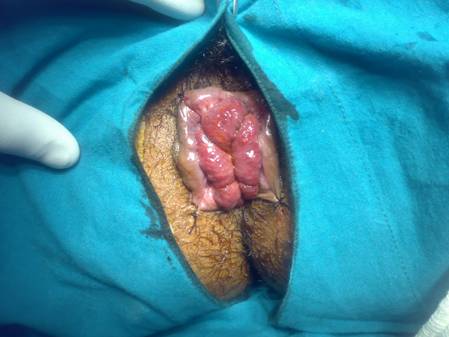
Conventionally, the Piles operation is done by Open method but now a new method is available which is more patient friendly and has better success rates. This procedure is called MIPH-Minimally Invasive Procedure for Haemorrhoids or Stapler technique.
What is done in Conventional/Traditional Surgery or Open method?
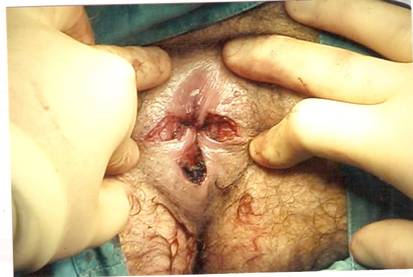
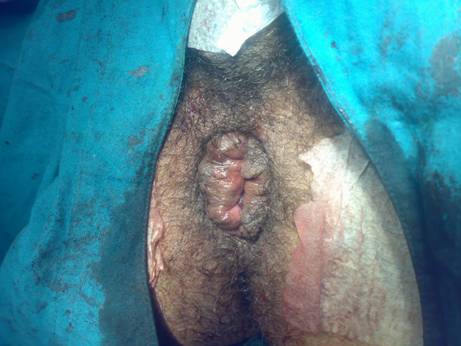
In Open method (Milligan-Morgan Technique), the bunch of dilated veins (piles) in the lower part of anal canal are dissected and then tied off. In order to avoid stenosis, three pear-shaped incisions are left open, separated by bridges of skin and mucosa. The dissection results in to a wound in the lower anal canal, which takes time to heal. Since the lower part of anal canal is highly sensitive to pain, the patient experiences agonizing pain for 4-5 post operative days. Therefore the patient is kept admitted in the hospital for 3-5 days. Normally the patient resumes work after 2-3 weeks when the wound is at least partially healed. The patient also needs to do hot water baths( Sitz bath) 2-4 times a day till the wound heals completely which usually takes 4-6 weeks.
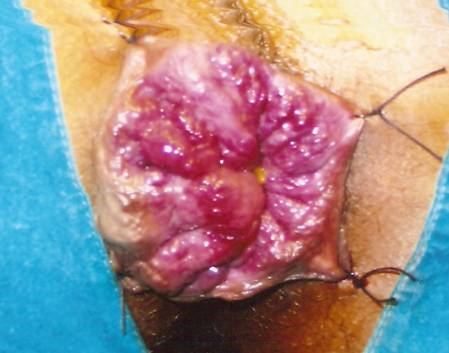
What is done in MIPH-Minimally Invasive Procedure for Haemorrhoids or Stapler technique?
MIPH is a technique developed in the early 90’s that reduces the prolapse of hemorrhoidal tissue by excising a band of the prolapsed anal mucosa membrane with the use of a circular stapling device In this technique, the pile mass is not directly operated or dissected. Instead the operation is done in the upper anal canal which is insensitive to pain. A disposable Stapler device is used which cuts the lining of the anal canal and sutures it back instantaneously. In the process, the blood supply to the pile mass is obliterated and this results in shriveling and hence disappearance of piles. Moreover the excess tissue is removed which corrects the mucosal prolapse and restores the hemorrhoidal tissue back to its original anatomical position…Read More
How can Piles be prevented?
Haemorrhoids are very common, and will occur anyway, but, as implied above, useful aspects of prevention are:
- Avoid becoming overweight, and lose weight if you are.
- Eat a high fibre diet.
- Exercise regularly.
Common Myths about Piles
MYTH 1:- Cure of piles not possible: The high recurrence rates of the conventional modes of treatment led to this belief. This is not true today. The newer method(Stapler Haemorrhoidectomy) has decreased the recurrence rates to the lowest levels.
MYTH 2:- Surgery of Piles is painful and prolonged: This was true with conventional surgery but with Stapler surgery, the treatment is virtually painless and can be done on day care basis(i.e the patient goes home the same day)
MYTH 3:- Piles always bleed: This is not true. A significant percentage of piles patients hardly bleed. They just feel the small masses(piles) in their anal area after motions. These masses gradually increase in size over years and may lead to complications of piles.
MYTH 4:- Piles can lead to cancer: Piles does not increase the risk of cancer but what is important to understand is that symptoms of piles and rectal cancer are same i.e bleeding off and on. So symptoms of piles can mask the presence of underlying rectal cancer. Therefore piles should always be treated even it is causing no symptoms other than occasional bleeding.
Myth 5 :- Piles is a taboo: Many people including the educated ones consider piles to be a taboo and do not come out openly/ discuss their problem. This can be dangerous. Piles is a simple disease like any other disease and a consultation should be sought with a good surgeon.
Myth 6: Piles treatment is a domain of quacks: As earlier mentioned, because of lack of satisfactory treatment with medical sciences, the treatment of piles was taken over by quacks especially in India. But now this tendency should be curbed as medical science offer very good treatment options or piles.