What is Anal Fistula Plug & how is this procedure done ?
Anal Fistula Plug is made up of sub mucosa of small intestine and is a highly sophisticated absorbable material which is absorbed/dissolved by the body in 6-8 weeks. This plug is placed and anchored in the fistula tract by a special technique and the internal opening is closed over it. It provides the scaffold over which body’s collagen gets deposited and closes the fistula. The Anal Fistula Plug(AFP) has been approved for clinical use by US FDA [United States Food & Drug Administration]-
What are the advantages & disadvantages of Anal Fistula Plug procedure?
ADVANTAGES

- Non-invasive- The procedure involves no cutting, scarring or distortion of anatomy at all.
- Little pain- The procedure is associated with comparatively little pain as there in no cutting involved.
- Early recovery- Recovery is very fast and the patient can be back to work with in a short span.
- Less morbidity- There is no new wound formation and no extensive post operative dressings are required.
- Short Hospitalization- The patient can usually be discharged in 12-24 hours after the procedure.
- Can be used again after a failure- In case of a failure, the procedure can be repeated without any risk or drawback.
- NO RISK of Incontinence- There is absolutely no risk of incontinence even in high fistulas and complex fistulas. Somebody has remarked ”For high Fistula, AFP method is a boon sent directly from heaven”.
- ‘Biological’ closure- This procedure is a biological closure of the fistula tract rather than a ‘Mechanical’ closure’ as in advancement flap.
- Minimal foreign body reaction- Studies have shown that there is minimal foreign body reaction to the plug material.
- Resistant to infection- The plug is made up of special material which is resistant to infection. This factor helps as the plug has to be placed in an infected environment.
- High Success rate – Studies have shown the success rate of Anal Fistula Plug treatment to be in the range of 70-87%.
- PROCEDURE OF CHOICE- The Anal Fistula Plug is the preferred treatment in
- High Fistula
- Long, complex fistulas
- Recurrent fistulas
- Horse-shoe fistulas,
- Anterior radial fistulas
- Crohn’s disease.
- Rectovaginal fistulas( Long term results awaited)
- Low fistula when patient doesn’t want pain, long hospitalization, delayed recovery and scarring.
DISADVANTAGES/Complications
- Higher Cost- The cost of the plug is on slightly higher side which becomes a deterrent for a few.
- Chances of Failure – Though Anal Fistula Plug has high success rate, still it is not successful in some patients. But even in these patient (with recurrence) , this procedure can be repeated without any harm/risk.
- Plug Extrusion- The plug can be extruded in 10-20% of cases.
- Abscess formation- There can be abscess formation in 4-8%.
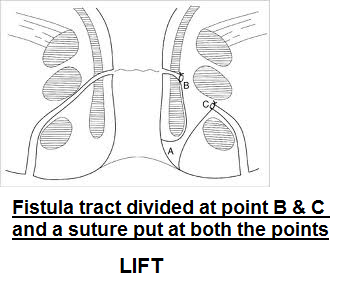
LIFT (Ligation of Inter-sphicteric Fistula Tract)
In LIFT procedure, the sphincter is not divided. A cut is given and a plane is developed between the two anal sphincters and the fistula tract passing between the two sphincter muscles is isolated. This portion of fistula tract between the sphincters is ligated (tied) and excised (cut out). The internal opening of the tract is cauterized and the portion of the fistula tract outside the sphincters is curretted, cleaned and left open so that it can drain freely and get healed.
VAAFT ( Video- Assisted Anal Fistula Treatment)
In VAAFT, a fistulascope is inserted through the external opening and the whole tract is visualized on camera. The internal opening is localized through the endoscope while visualizing the ano-rectum from outside. After this, two stitches are taken through the internal opening so as to isolate the internal opening. After this, the fistula tract is cauterized with a monopolar cautery electrode so as to coagulate (burn) the fistula mucosa (lining) from internal opening to the external opening. The necrotic burnt tissue is taken out with the help of a brush and forceps. After this, the internal opening is lifted with the help of two stitches taken earlier and closed with a linear cutting Stapler which closes the tract at the level of the internal opening.


